Ten great uses of existing technology have made the shortlist for the Best Application of Technology category at the Digital Construction Awards 2026.
This category recognises the most effective application of a specific existing technology. Existing means a product (hardware or software) that has been available on the market for more than 18 months. As ever, this category was extremely popular, attracting many excellent entries. Here are the 10 that have made the shortlist.
Digital estate management platform | Danske Bank/RLB Digital
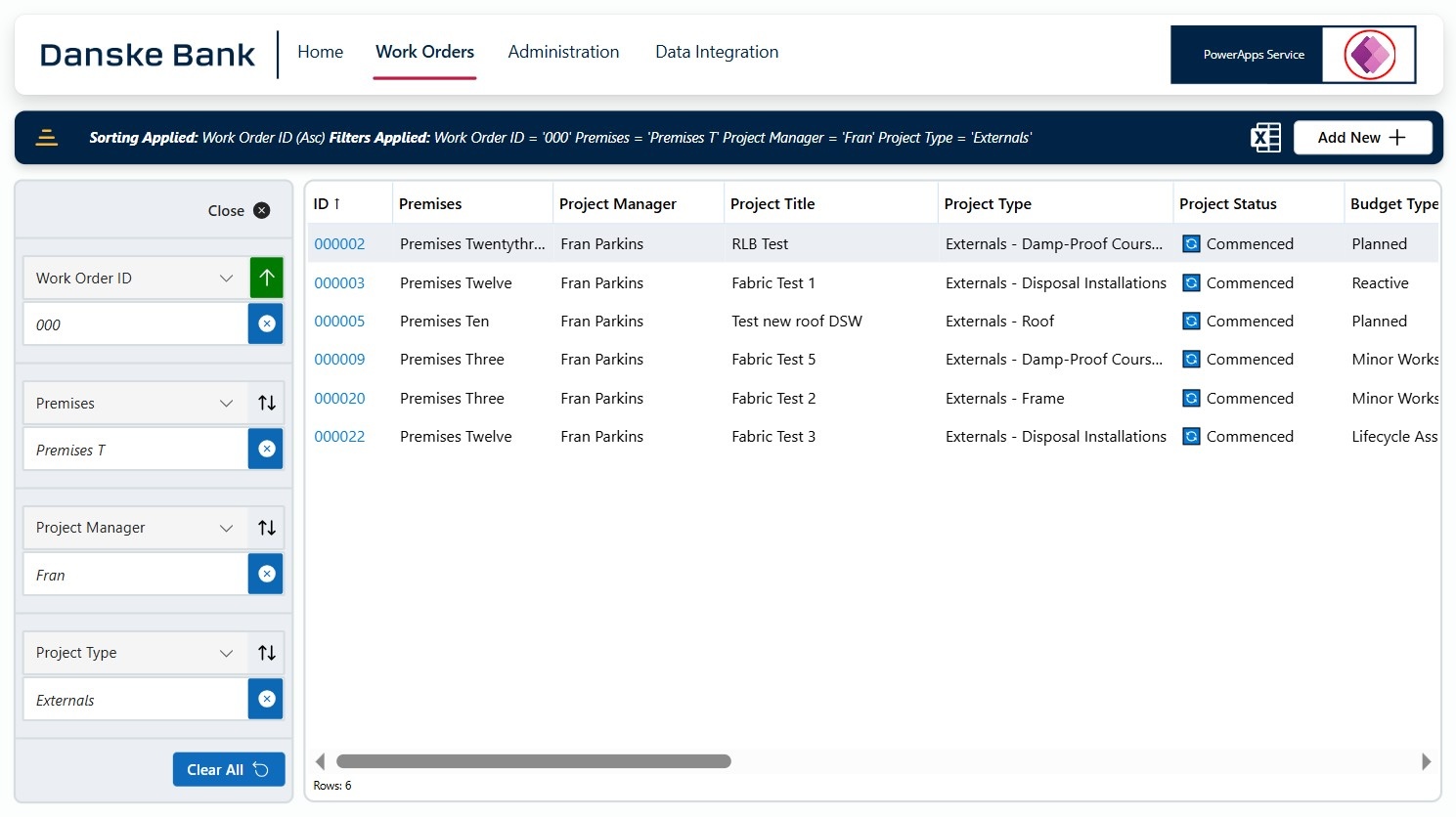
Danske Bank’s Property Services team manages a huge budget for capital projects, facilities, energy and estate management. A strategic review revealed that property and asset data was scattered across spreadsheets, static reports and legacy systems. Financial processes were manual, time‑consuming and produced inconsistent reporting.
To overcome this fragmented approach, RLB Digital built a connected digital estate management platform on Microsoft Power Platform. Using Power Apps, Power BI and Dataverse, the team replaced legacy MS Access and Excel tools with a low-code, centralised system that integrates financial information, asset performance and lifecycle forecasting.
Power App captures project, vendor and financial data, while an embedded Power BI dashboard provides live analytics, allowing users to edit records without switching applications. Integration with Dynamics 365, SharePoint and Autodesk Construction Cloud creates a seamless workflow for approvals, document management and payments. An agile, phased rollout ensured robust governance, role‑based permissions and performance optimisation.
The unified platform eliminates duplication, reduces administrative effort and improves data accuracy. Automated reporting cuts monthly reconciliation time by more than 60%, delivering real‑time visibility of expenditures and commitments. Users now raise, approve and track projects within a single, intuitive interface, fostering strong adoption and supporting Danske Bank’s digital strategy while providing a scalable foundation for future innovations.
Digitising site operations at scale | Hill Group/innDex
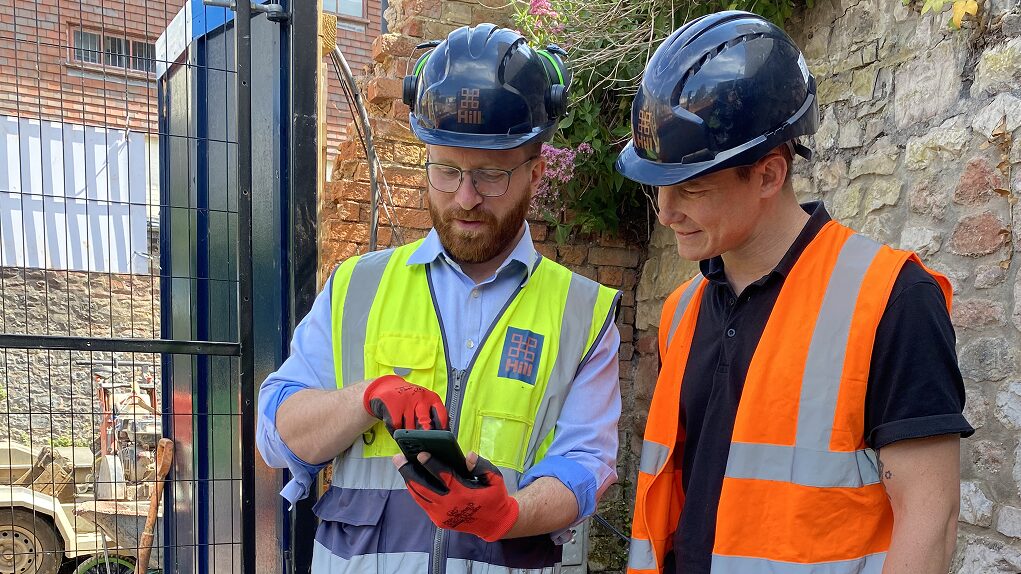

Housebuilder Hill Group partnered with cloud-based construction project management software innDex to digitise its core site operations across more than 60 live projects and a workforce of up to 5,000 daily operatives.
Paper‑based inductions, manual permit sign‑offs and fragmented access‑control systems created inconsistent safety standards, lengthy approval times and a high administrative burden. Managers often had to travel across large, multistorey sites to authorise work, leading to delays, while tracking who was on site was unreliable.
InnDex delivered a purpose-built digital workforce and site management platform that links every step of the site entry process. Workers complete digital inductions and upload qualifications before arrival. Approved profiles automatically unlock turnstiles or mobile‑verification entry. Permits are created, signed and closed from a mobile device, with photos, time stamps and digital signatures, cutting approval time from hours to minutes.
Integrated facial recognition or mobile verification enforces entry only for authorised workers. In‑app messaging replaces notice boards, providing instant safety alerts with read‑receipt tracking. All data feeds a daily Power BI dashboard that shows workforce numbers, trades, permit status and site attendance in real-time.
Outcomes of this implementation include more than 360,000 inductions logged – saving the equivalent of one site manager’s day per week per site – and more than 2,700 digital permits issued, reducing approval time by up to 50 minutes each.
Additionally, instant, tracked communication has boosted safety brief compliance, and daily dashboards have given leadership immediate visibility for resource allocation and risk mitigation.
Halve the Half: the no- and low-cost opportunity to reduce cost and carbon | Cardiff Metropolitan University

Cardiff Metropolitan University’s estate ran on standard automated meter reading (AMR) data that showed a large share of energy was being consumed when buildings were virtually empty. With mounting financial and net‑zero pressures, the university needed an immediate, low‑cost way to cut out‑of‑hours energy use without impacting comfort, teaching, research or residential life. Existing BMS controls were in place, but underused. On top of that, estate teams had been conditioned to avoid criticism, making organisational culture the biggest challenge.
The team adopted a ‘see‑act‑prove’ cycle using only the data and controls already available. AMR data was analysed in lightweight Excel models to rank buildings by total and out‑of‑hours consumption. Visualisations highlighted the worst performers. An energy manager then reset BMS schedules, fixed rogue timers, recalibrated setpoints, recommissioned drifted plant, cleaned filters and tightened domestic hot‑water regimes – all low‑ or no‑cost measures.
Changes were verified instantly against the same AMR feed, allowing rapid iteration and ensuring daytime comfort remained unchanged. The approach avoided any capital‑intensive upgrades, relying solely on existing meters, BMS and simple analytics.
During the academic year to 31 July 2025, gas use fell by 22.3%, electricity by 7.5% and water by 11.3% compared to the previous year. In absolute terms, the university saved 2.GWh of energy and approximately 10,000 cu m of water. Financially, the initiative resulted in around £700,000 in-year savings (adjusted for tariff reductions) and delivered immediate opex payback, freed budget for core missions and sparked a sector‑wide pilot across 12 UK universities to replicate the methodology.
Kier Construction’s use of Fuzor 4D construction sequencing on the Haleon Innovation Facility
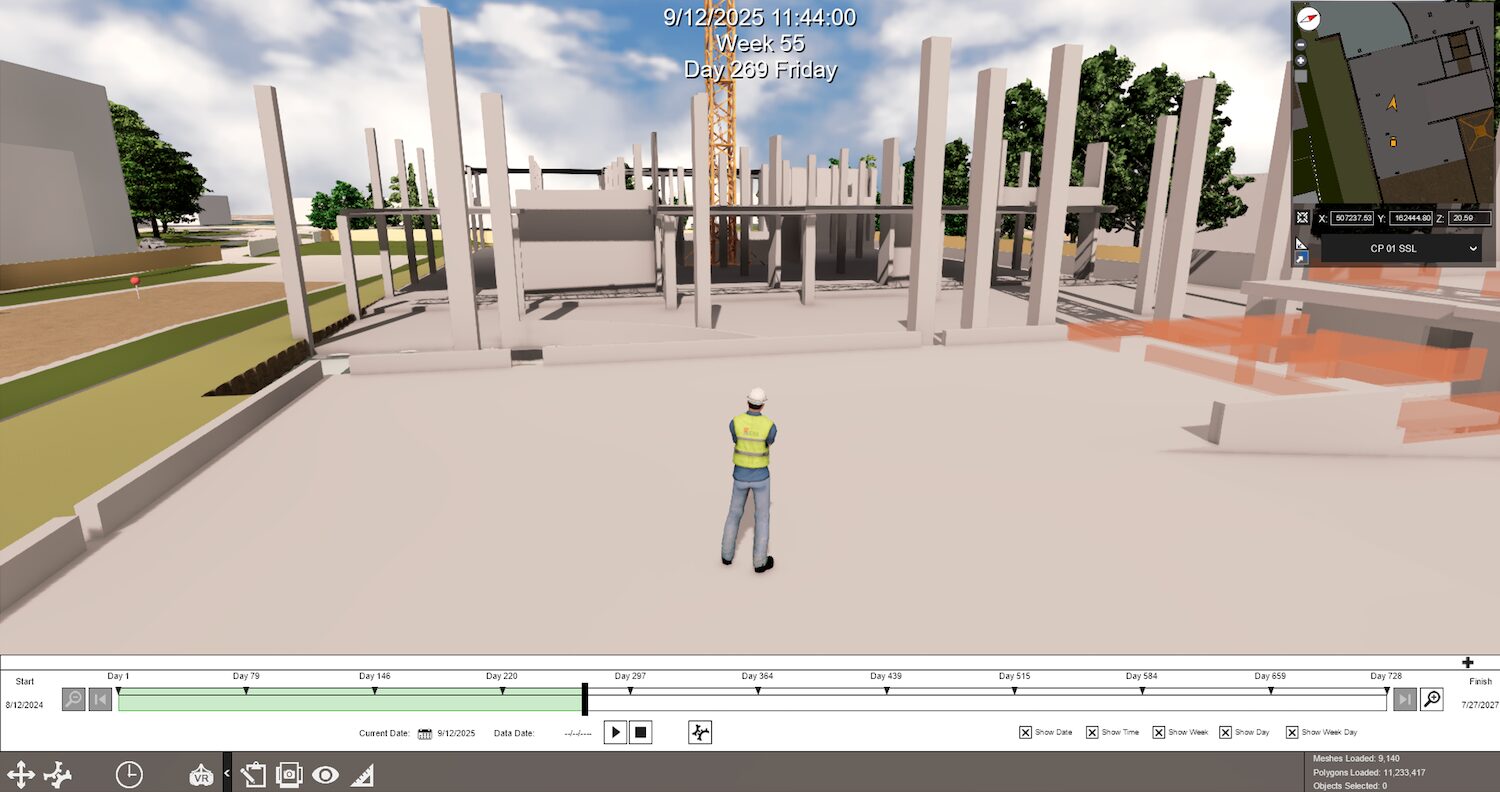
Kier’s delivery of complex construction projects was hampered by several issues: traditional 4D visualisation cost between £5,000 and £20,000 for only a few minutes of static video, which was expensive, hard to update and lacked editable master files. Internal staff with advanced digital skills were underused, wasting innovation potential. Clients increasingly demanded 4D sequencing in contracts to validate high‑risk construction sequences, while market pressure made outsourcing 4D services prohibitively costly and inflexible, limiting rapid prototyping and real‑time adjustments.
To bypass these challenges, Kier adopted Fuzor 4D Construction Sequencing on the Haleon Innovation Facility. Fuzor was chosen for its interactive, flexible and cost‑effective approach. Existing 3D models and construction programmes were integrated, and internal teams were upskilled to use the software, including AI‑driven allocation of work breakdown structure elements.
The platform enabled virtual site walks, day‑by‑day navigation, rapid prototyping and quick value engineering changes. Workflow adaptations and training addressed initial challenges, while lessons learned were fed into subsequent projects.
The switch to Fuzor cut outsourced 4D visualisation spend by 74% and gave Kier an internal capability that met client requirements at a fraction of the former cost. Interactive models improved stakeholder engagement, health and safety rehearsals and logistics planning. These efficiencies contributed to on‑time, on‑budget delivery and differentiated Kier in the market, receiving strong client and team feedback.
Mynydd Isa Campus – delivering net-zero in operation school campus | Arup/IESVE
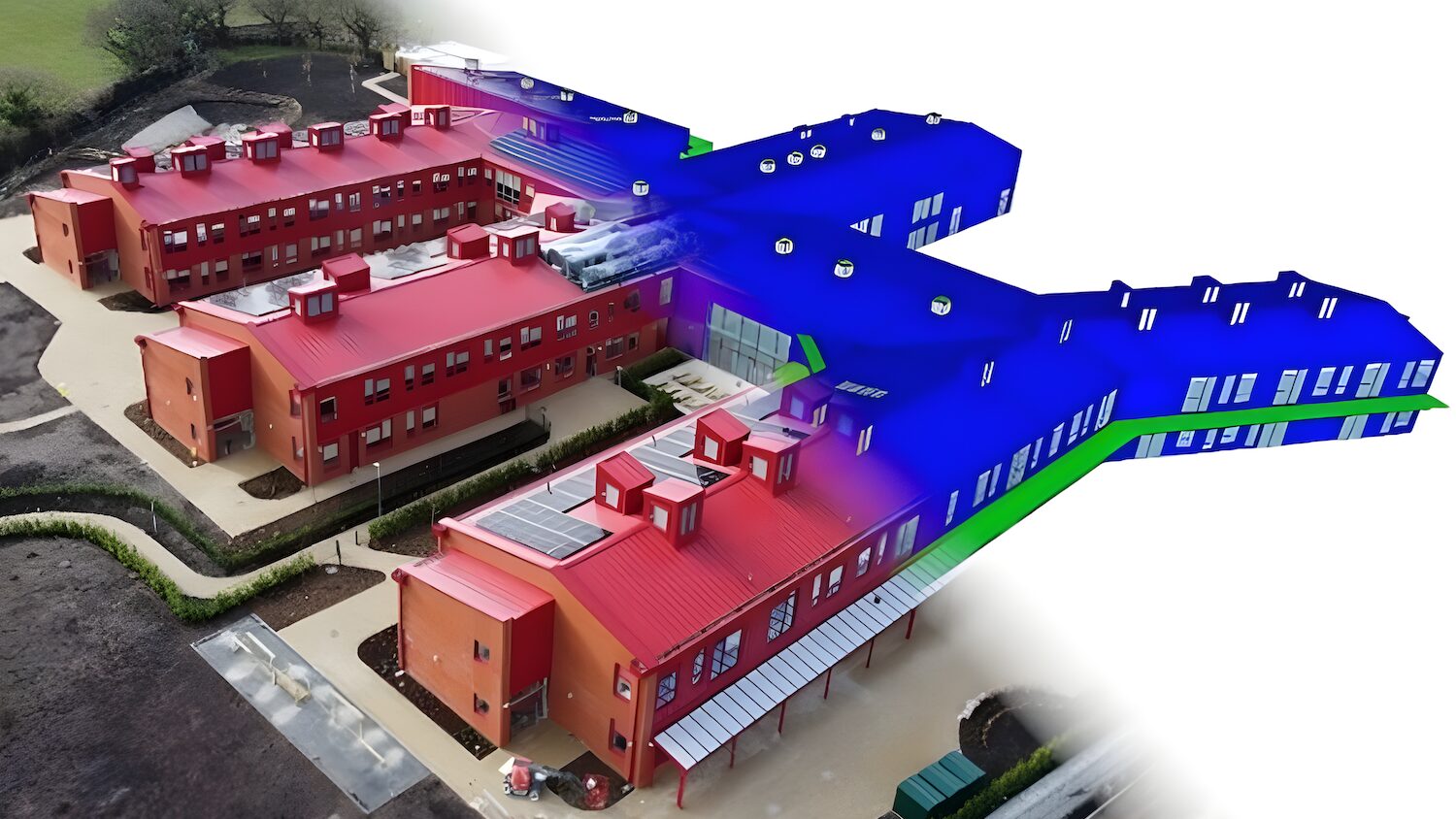

The Mynydd Isa Campus was commissioned to serve 1,300 pupils while achieving net-zero carbon in operation, a BREEAM ‘Excellent’ rating and 25‑year performance resilience to a +2°C future climate change scenario. Standard compliance modelling could not reliably predict long‑term energy use, unregulated loads or the effectiveness of natural/dual‑mode ventilation needed to avoid mechanical cooling. Uncertainty around occupant behaviour and build quality variations (airtightness, commissioning) threatened the ambitious carbon and comfort targets.
Arup’s building physics team selected the software platform IESVE for its dynamic, physics‑based simulation capability. It enabled parametric testing of glazing, airtightness, natural/ventilation strategies, heating/cooling loads and integration of a 1,080‑panel rooftop PV system.
The platform modelled unregulated energy uses, future climate files and occupant behaviour sensitivity in a single environment. Conservative build quality scenarios were run, and close collaboration with the contractor refined onsite targets for airtightness and system commissioning. Results guided the dual‑mode ventilation design, heat recovery and electrical control strategy.
The campus opened last year as Flintshire’s first net-zero carbon in operation school, meeting the BREEAM ‘Excellent’ rating. The rooftop PV installation generates more than 500,000kWh annually, exporting surplus energy during summer and reducing annual CO2 emissions by more than 100 tonnes.
The building operates without mechanical cooling, maintains thermal comfort under future climate conditions, and provides Flintshire County Council with lower operating costs, verified performance and a low‑carbon learning environment.
Oxford Science Park | Tarmac/J Coffey Construction/Mace
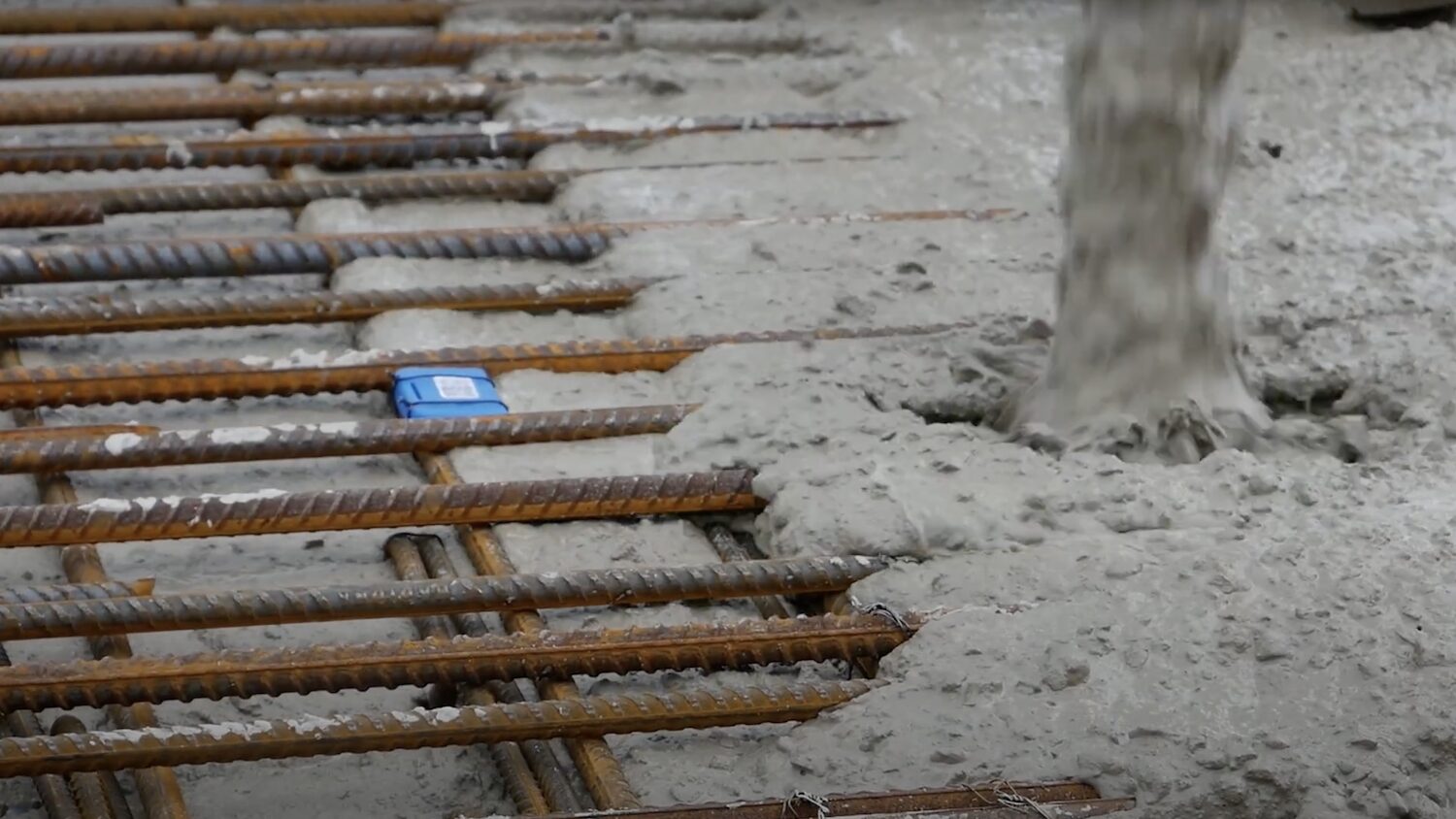

The new 42,000 sq m Oxford Science Park development required air‑source heat pumps, renewable energy and advanced ventilation to meet its sustainability targets. Yet the specified high early-strength Portland cement concrete for reinforced slabs carried a large carbon footprint, threatening the project’s environmental goals.
Tarmac and J Coffey Construction teamed up to deploy Tarmac’s CEVO digital concrete platform, combining low‑carbon Portland limestone cement‑based mixes (30%‑50 % ground granulated blast furnace slag) with MixAI predictive optimisation and 53 embedded Converge maturity sensors.
MixAI forecasted strength and durability before placement, allowing selection of the lowest‑carbon mix that still met structural requirements. Real-time data transmitted from the onsite embedded concrete sensors enabled complete control of the building programme and material specification.
With this maturity data, the project team could validate performance and understand exactly what strength the concrete would achieve for the ambient temperature at the time. These insights gave Tarmac the possibility to choose the most suitable mix that had the lowest carbon value possible, without impacting programme strength or quality.
In total, more than 535 tonnes of CO2 were saved, compared with the original specification, equating to 38% savings and delivering a total carbon footprint of 869 tonnes of CO2 instead of the initially predicted 1,404 tonnes.
Powering safer sites: applying Microsoft Power Platform to transform daily briefings | Laing O’Rourke

On large construction sites, Laing O’Rourke’s supervisors run daily activity briefings (DABS) that traditionally relied on paper and manual processes. With hundreds of operatives and multiple gates, these processes were time-consuming, inconsistent and hard to audit. The challenge was to make the process faster, more transparent and more auditable while maintaining compliance with ISO 45001 and the golden thread.
Laing O’Rourke’s digital team came up with the solution: a fully integrated e‑DABS suite built on the Microsoft Power platform. A Power App digitises the briefing sheet, pulls live clock‑in data from turnstile data stored in a SQL database, and captures digital signatures or QR code scans.
Power Automate sends an alert at 10am each day for any unbriefed operatives. All records are stored in Dataverse, while point-of-work risk assessment (PoWRA) entries are analysed by Copilot Studio agents that summarise recurring risks and auto‑update RAMS. A conversational Copilot bot lets users query the Dataverse. Power BI dashboards visualise briefing completion, safety trends and workforce engagement. The development used existing Microsoft 365 licences and an agile sprint approach, piloted on the HS2 M42 Twin Box and Plot B2.
Supervisors now complete briefings in the app, saving 10‑15 minutes per shift and delivering approximately £200,000 cumulative annual admin savings across projects. The structured PoWRA data has generated more than 200 lessons learnt entries that the Copilot Studio AI agent has summarised into digestible insights. These are automatically fed back to RAMS owners, resulting in faster document updates and a 15% reduction in near-miss incidents.
The platform’s reusable architecture enables rapid rollout of related safety tools, resulting in up to an 80% reduction in future development costs.
Reality capture at scale in response to the BSA | Morgan Sindall Construction/Oculo AI
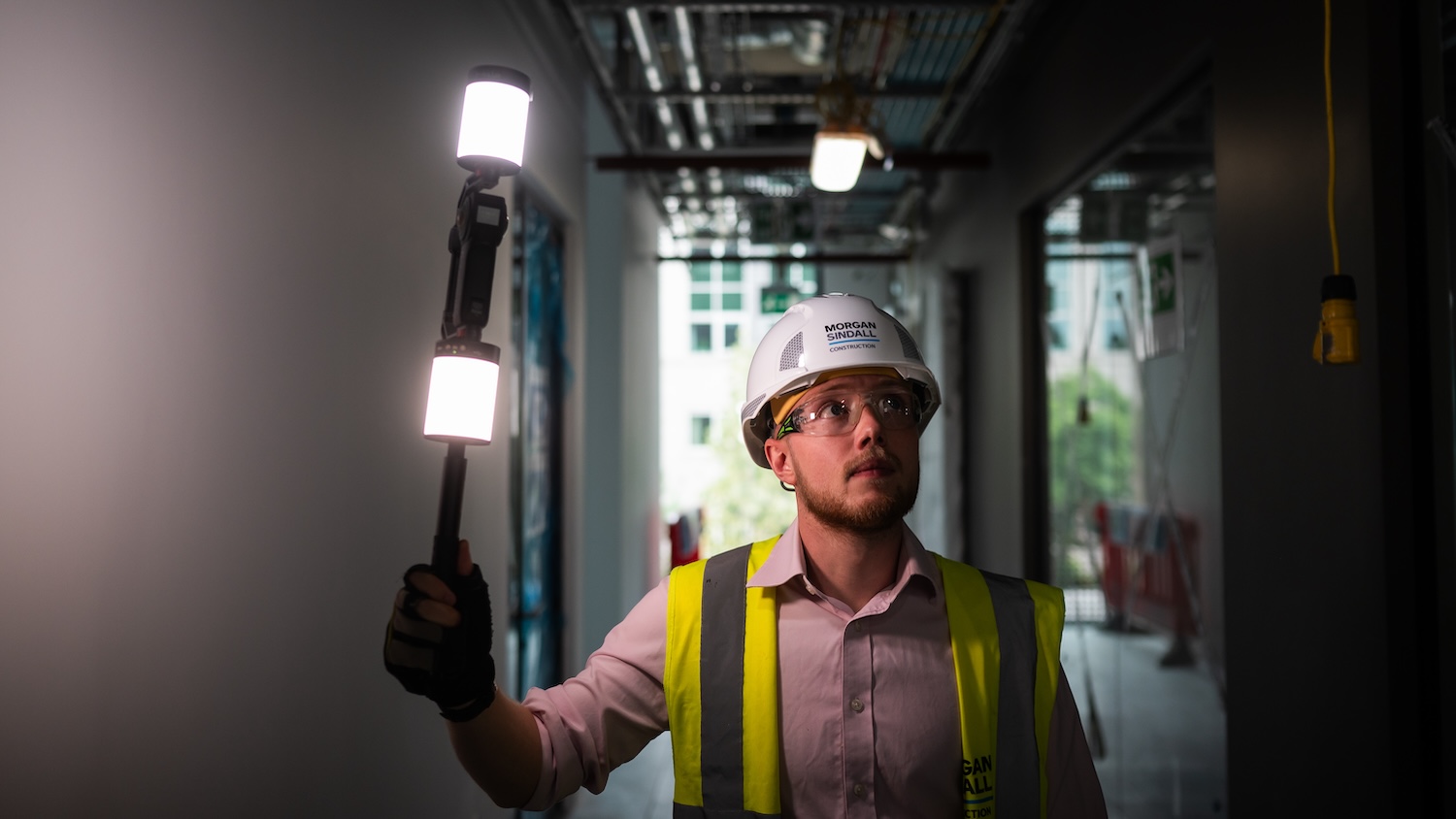

Morgan Sindall Construction needed a scalable way to capture and manage onsite visual information to meet the Building Safety Act, improve design coordination and reduce costly rework.
Existing methods, such as photos, snag lists and site diaries, produced fragmented, hard-to-navigate records and did not provide the structured, remote‑viewable documentation required for modern project assurance across its £1bn-plus annual active portfolio.
After evaluating 14 reality capture tools, Morgan Sindall partnered with Oculo AI under a multi‑year enterprise agreement. Oculo’s 360° cameras create navigable digital site records (similar to Google Street View for construction sites) that overlay BIM models, highlight deviations and generate automated reports.
The rollout included custom developments: BIM overlay, GDPR‑compliant full body‑blurring, an automated capture dashboard and AI‑driven progress analytics. Training, a dedicated mounting system, upgraded connectivity (from 5G to fibre or Starlink) and lighting rigs ensured high‑quality imaging. Symetri acted as implementation partner, providing onboarding and support for 200-plus sites and more than 8,000 scans completed.
The platform transformed operations: early detection of as‑built versus as‑designed mismatches, remote desktop reviews that cut travel, and compliance documentation for the Building Safety Act.
It has also resulted in average resource savings of two hours per week per project, equating to 22,540 hours across 200 projects. Rework costs fell sharply and issue resolution was quicker. The digital foundation now supports Morgan Sindall’s ‘Perfect Delivery’ philosophy, scalable progress tracking and broader responsible business goals.
Transforming nuclear safety through digital integration | AtkinsRéalis/Sellafield
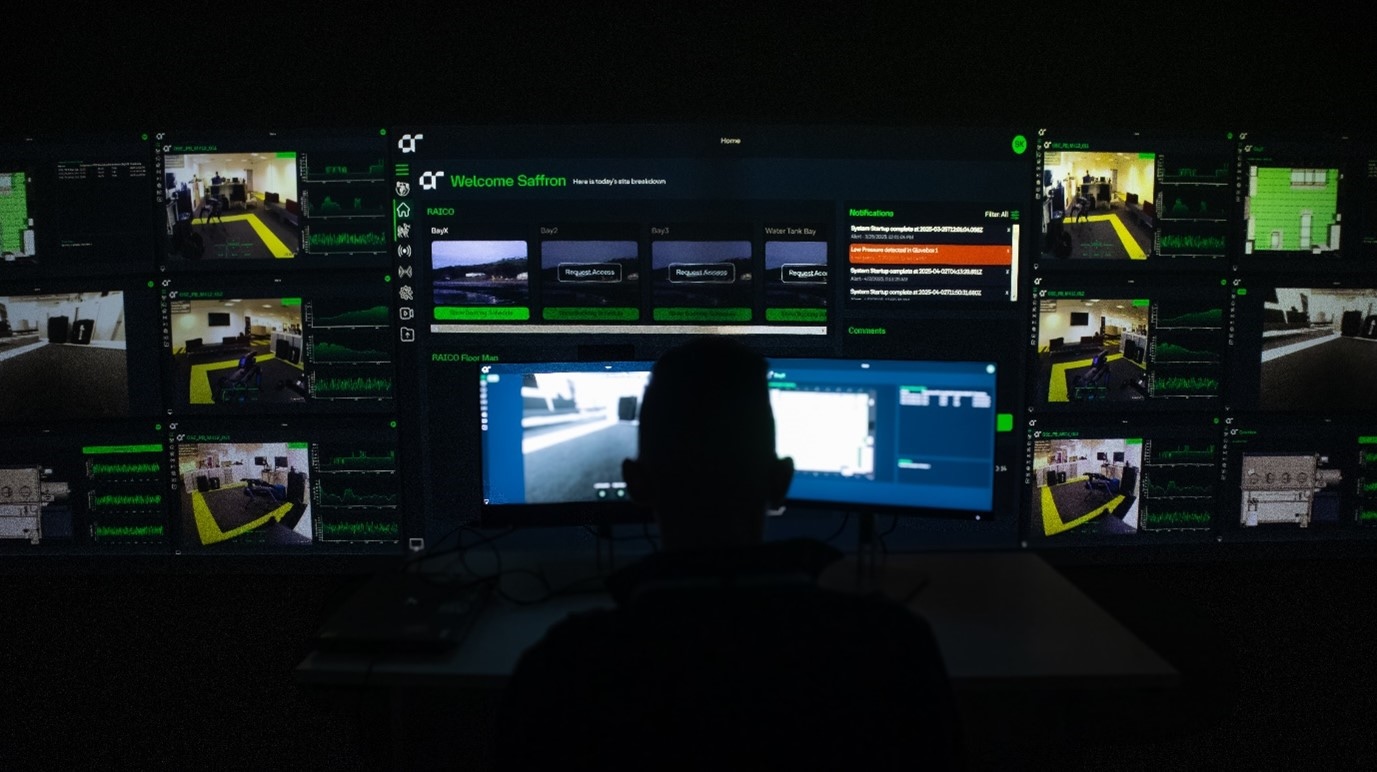
Sellafield, one of the UK’s most complex nuclear sites, wanted to demonstrate real-time visibility, integrated emergency response and collaborative tools. Strict compliance and security requirements made digital change risky. The site needed to address three issues: how could technology boost safety and response times; could facility data be collected and analysed live; and how could any new solution remain secure and manageable?
AtkinsRéalis, together with robotics manufacturer ICE9 and emerging sensor tech company Createc, built Industry X: a demonstrator that fuses IoT sensors, robotics, AI and cloud services into a single Azure-hosted web platform.
The dashboard allows operators to explore site maps, view live temperature, humidity and radiation readings, watch pan-tilt-zoom camera feeds and control robots such as Boston Dynamics’ Spot and CARMA2.
A Raspberry Pi‑based telemetry data relay encrypts sensor streams to the cloud, while an Edge PC (Jetson Orin Nano) processes data locally for continuity during network loss. An AI‑driven LLM assistant answers procedural queries and can trigger alerts or open reports. Emergency‑scenario scripts automatically raise alerts, display sensor data, provide checklists and launch Microsoft Teams collaboration – all within the same interface. End‑to‑end encryption, UK‑based Azure hosting and secure edge gateways ensure a stringent security regime.
Industry X delivered a unified, user‑friendly control centre that eliminated the need for multiple disconnected systems, improving situational awareness and decision‑making during incidents. The intuitive interface made advanced technology accessible to all staff, while automated alerts and AI assistance accelerated emergency response. Edge resilience ensured operations continued during internet outages.
A recent Sellafield research, development and innovation review estimated that the potential annual savings could exceed £130m. The success of Phase 1 has already led to Phase 2, which will introduce AI-driven analytics, XR integration and autonomous data collection.
Transforming workforce management through digital integration | MSite
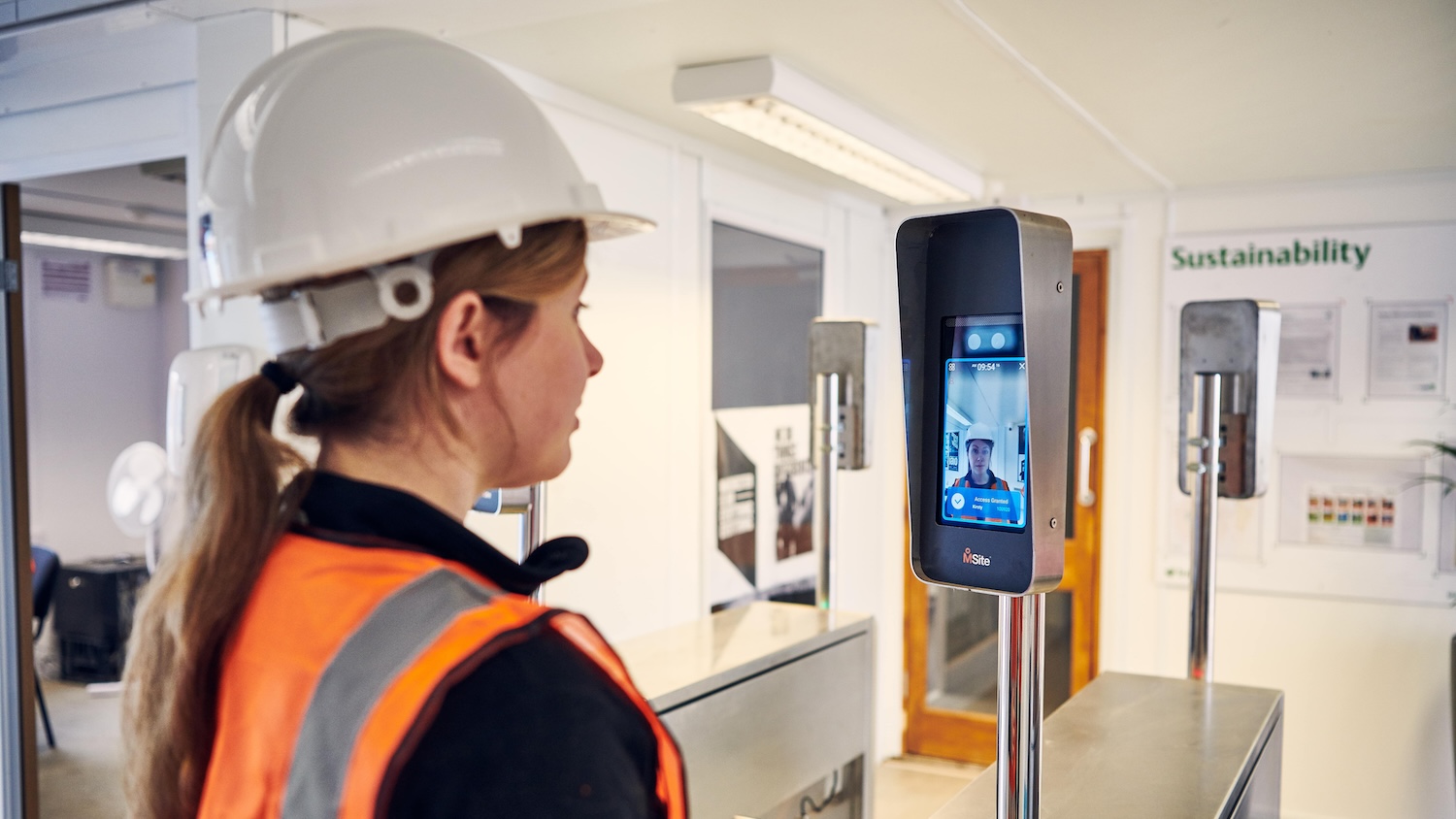

Many construction sites in the UK still rely on fragmented, manual and paper‑based processes for onboarding, compliance checks, access control and reporting. This duplication creates human error, inconsistent data and makes it challenging to prove compliance with diverse legislation requirements.
To bypass these challenges, MSite introduced a unified workforce management platform that digitises the entire worker journey: pre-site, onsite and in-site. A single ‘one worker profile’ stores right‑to‑work, CSCS, visas and other credentials, enabling remote pre-registration and multi-lingual online inductions.
Biometric access control, facial recognition pods and automated briefing logs enforce onsite verification and fatigue monitoring. Integrated dashboards (Power BI, Autodesk and Procore) convert captured data into live analytics for safety, productivity, ESG and social value reporting.
The platform supported 2,643 projects between January and November 2025, and 168 Tier 1 and Tier 2 contractors (including Balfour Beatty, Morgan Sindall, Vinci and Galliford Try), representing more than £11m in sales. The system also created more than 400,000 verified worker profiles, processed 96 million transactions, and captured 100 million labour hours, providing a secure, traceable audit trail that supports compliance with the Building Safety Act and modern slavery legislation.
Celebrate with the best
The winner will be revealed at the gala dinner at the London Marriott Grosvenor Square on 18 March. You can join the shortlisted entrants by booking your seats at the awards.
The Digital Construction Awards are organised by Digital Construction Week, the Chartered Institute of Building, CM and Digital Construction Plus. Bluebeam, nima and Sage are among the sponsors.
To find out more about the awards, head to digitalconstructionawards.co.uk.
To become an awards sponsor, email Karolina Orecchini.
Keep up to date with DC+: sign up for the midweek newsletter.